- Product Overview
- Laser module is a device or system which generates refined beam size, line length or pattern beam designed for an industrial and military customer. Dot, line, cross line beam generators are main products of Lanics.
- Characteristics
-
특징 Monochromatism consisting of a single wavelength or color, and emitted in a narrow beam. This contrasts with common light sources, such as the incandescent light bulb or LED which emit incoherent photons in almost all directions, usually over a wide spectrum of wavelengths. 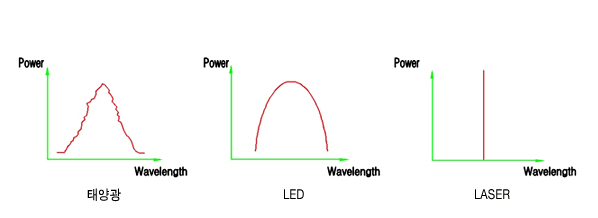
Coherence and
Interferencethe property of wave-like states that enables them to exhibit interference. It is also the parameter that quantifies the quality of the interference (also known as the degree of coherence). It was originally introduced in connection with Young’s double-slit experiment in optics but is now used in any field that involves waves, such as acoustics, electrical engineering, neuroscience, and quantum physics. In interference, at least two wave-like entities are combined and depending on the relative phase between them, they can add constructively or subtract destructively. The degree of coherence is equal to the interference visibility, a measure of how perfectly the waves can cancel due to destructive interference. Because of coherence, the beam has good directivity. High Energy Density
and BrightnessDue to the coherence and monochcomatism, the laser module has high energy density and brightness.
- Type and class of the lens
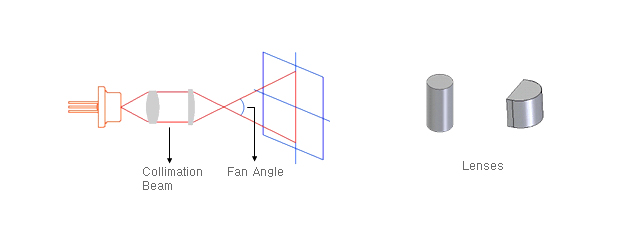
- Collimator lens collects a diversied beam to collimate and line generator spread collimated beam to make a sharp line beam.
Collimator lens to make a dot beam are as listed below. -
Type and class of the lens Type Lens Remark Collimator(for Dot) spherical, non-spherical Collimation or focusing beam Line Generato Deflection lens
Cylinder,Cylindrical lens45 degree (short range)
10,15,30,45,60,90,120 degreeCross Line Generator Deflectioon lens
Diffraction lens
Cylinder,Cylindrical lens45degree (short range)
5degree (short range)
10,15,30,45,60,90,120 degree* Cylinder, cylindrical lens locates after the collimator.
- LD driver and circuit
- LD is an abbreviation of Laser Diode, and called semiconductor diode. After conjunction of P-type and N-type semiconductor, positive bias at P-type and negative bias at N-type make high energy gap which derives the combination of holes and electrons to radiate the light. The light amplified by resonator is a Laser. LD is a simple PN junction PN semiconductor and the light is amplified by the polished surface of light source.LD is very sensitive with current and circuit must be designed to drive proper current. Two types of circuit are currently in common. APC is an abbreviation of Automatic Power Control. LD generates laser when the proper current is supplied to the device in the specified temperature. If the unstable current causes increase of junction temperature, the output power decreases, and hight emperature even break the LD junction. To prevent and compensate this phenomena circuit monitors the output power of LD and regulates the current. ACC is an abbreviation of Automatic Current Control, APC circuit supplies only specified current without output power monitoring. ACC is usually applied to the pulse laser drive.
-
Advantage of LD
- 01Small and
light weigh - 02High
efficiency - 03High frequency
modulation of
upto 10GHz - 04Long life time,
high reliablity - 05Various
wavelengths
- 01Small and
- LD Structure
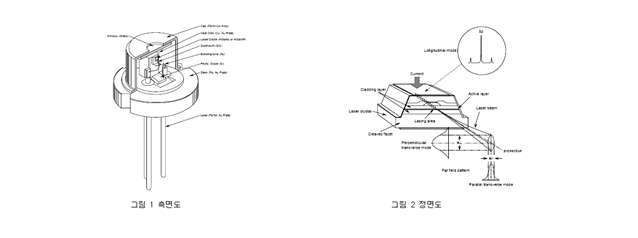
- Picture1 is structure of TO-18 and TO-5, picture2 shows laser generation of picture1
-
LD Structure Type Size TO-18 5.6Ø TO-5 9Ø TO-3 eclipse HHL rectangular - Picture1 shows the window glass under cap and LD chip located on the substrate. To radiates the heat, heat sink mounted under submount. Lasing on the chip is described in the picture2, biased current generates laser on both side of active layer. Diffraction casuesd by narrow active layer derives the beam shape of eclipse with different colunm length and row length. Laser beam is monitored by internal photo diode to provide monitoring signal.
- Distinction of P-type LD and N-type LD
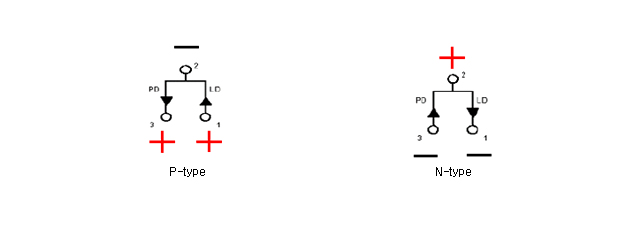
- In LD spec sheet, LD is distinguished to P and N type. When the case of LD must be connected to ground, it is a p-type, vise versa.
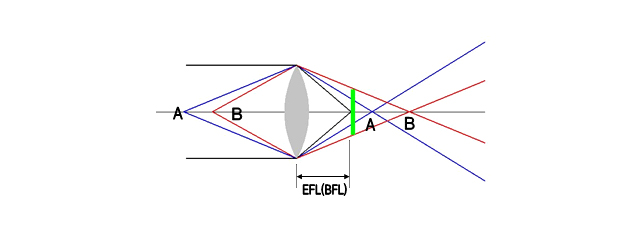
- Focal Length of Lens
- For a thin double convex lens, all parallel rays will be focused to a point referred to as the principal focal point. The distance from the lens to that point is the principal focal length f of the lens. For a double concave lens where the rays are diverged, the principal focal length is the distance at which the back-projected rays would come together and it is given a negative sign If LD is located at the BFL of lens, parallel lay can be transmitted. However, because of spherical aberration, different beam divergence angle, and astigmatism collimation is not easy. Focus theorem is as picture below
- Line beam generation and beam width
- With assumption of parallel beam incident from collimator to cylinder lens, the beam transmits as following trace. Because cylinder lens is spherical at only one side, incident beam has curvature about only one axis, which decide length of line beam. About another axis beam transmit directly, which decide beam width, line beam can be generated. Following picture shows the lens shape. If the incident beam is controlled to focus at the first surface of the cylinder lens, beam size can be varied. Which is how to control the beam width and length